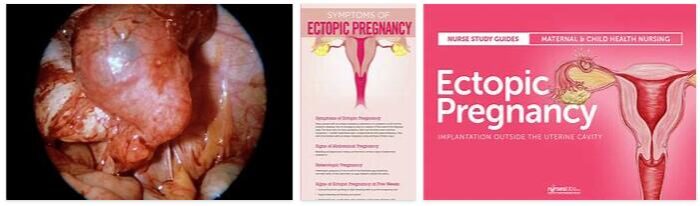
According to foodanddrinkjournal.com, an ectopic pregnancy, also known as ectopic pregnancy is called, describes the situation of a non-nested in the uterine cavity embryo. Mainly it is the so-called ectopic pregnancy; however, the embryo can also implant in the abdominal cavity or in the ovaries. Unless implantation takes place in the abdominal cavity, the embryo cannot survive.
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
If there is an ectopic pregnancy, the embryo has not implanted in the uterine cavity, but outside – for example in the fallopian tube, in the ovary or in the abdominal cavity. The most common form is ectopic pregnancy. The egg has already divided several times, whereby the cells have accumulated in a spherical shape (morula).
If there is a change in the fallopian tube, the fruit migrates slowly, so that it reaches the implantation stage before it reaches the uterine cavity. Ovarian pregnancy is very rare. So-called ovarian pregnancy is found in one in 40,000 pregnant women.
Because the fallopian tubes and ovaries are not firmly connected, the fertilized egg can also migrate into the abdominal cavity and implant itself in the peritoneum. Such pregnancies go unnoticed for a long time because there is enough space for growth. If the egg nests in the cervix, the doctor speaks of a cervical pregnancy (cervical pregnancy). Such pregnancies are extremely rare.
Causes
Pre-existing conditions and other factors can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy. These include, for example, inflammation of the fallopian tubes or ovaries caused by sexually transmitted diseases (chlamydia).
Due to the inflammation, the cilia can be damaged. These can ensure that the egg, which is located in the fallopian tube, moves quickly enough into the uterine cavity. Sometimes the fallopian tubes can also stick together. The egg gets caught or can get stuck in the constriction.
In some cases, the fallopian tubes can be too long; Malformations or muscle impairment are also reasons why the fertilized egg does not get into the uterine cavity in time. Other risk factors include previously suffered miscarriages, operations on the uterus, operations in the abdomen or abortions.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
The symptoms that occur in the context of an ectopic pregnancy are barely noticeable at the beginning; in many cases, the patients do not have any symptoms indicating an ectopic pregnancy. A feeling of tension in the breasts, a missed period, frequent urination, vomiting, nausea and severe pelvic pain are possible. Occasionally there may be slight vaginal bleeding.
Diagnosis & course
If you are known to be pregnant or if you have missed your period, with symptoms associated with an extrauterine pregnancy, a gynecologist should be contacted as soon as possible. The gynecologist will first ask about the medical history; the doctor will then carry out palpation examinations.
The palpation examinations can lead to pain in the uterus and / or in the abdomen. If it is suspected that an ectopic pregnancy is present, an ultrasound examination follows. Urine and blood are also examined, paying attention to the beta-HCG.
Beta-HCG is the value that provides information about whether or not you are pregnant. Even if the gynecologist is not 100 percent sure whether it is actually an extrauterine pregnancy, he will have the patient referred to a hospital at the slightest suspicion.
Ectopic pregnancy often leads to life-threatening complications for those affected. The ectopic pregnancy in the first trimester of pregnancy is still the most common cause of death in pregnant women. For this reason, the pregnancy must be terminated immediately if the doctor determines an ectopic pregnancy.
Complications
Ectopic pregnancy has a negative effect on the patient both physically and psychologically and can complicate life as a whole. In most cases, the ectopic pregnancy is not recognized by those affected. There is only a feeling of tension in the breasts, vomiting and nausea. Most of the time there is no period.
In some cases, however, vaginal bleeding may occur. The ectopic pregnancy must be determined by the gynecologist. The treatment depends on the respective options. The doctor can perform surgery to remove the fruit. However, it cannot be guaranteed that the fallopian tubes will not have to be removed as well.
If the fallopian tubes remain intact, a new ectopic pregnancy cannot be ruled out. In severe cases, it is necessary to remove the uterus. With the uterus or fallopian tubes removed, it is no longer possible for the woman to give birth. This leads to severe psychological problems and depression in most people.
The partner is also indirectly affected by the ectopic pregnancy and suffers from psychological problems. Therapy and discussions with a psychologist can be helpful here. In most cases, the mental illness can be overcome so that there are no further complications.
When should you go to the doctor?
An ectopic pregnancy must always be treated by a doctor. However, this disease usually results in the death of the unborn child. Those affected should always consult a doctor if there is a very strong feeling of tension in the breasts during pregnancy. The period is also usually absent and those affected suffer from strong mood swings or irritability.
Furthermore, an increased urge to urinate can also indicate the ectopic pregnancy and should be examined by a doctor. Vomiting and nausea are symptoms of the disease and must be examined by a doctor if they occur over a long period of time. This can also lead to severe pain in the lower part of the abdomen.
As a rule, a gynecologist or the hospital is consulted in the event of an ectopic pregnancy. Those affected are then dependent on immediate treatment so that there are no further complications. The disease can be recognized and diagnosed at an early stage through regular examinations. As a rule, the life expectancy of women is not reduced.
Treatment & Therapy
If the doctor makes a diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy, there are two options: surgery or medication. If the doctor decides to have an operation, he removes the fruit and tries to preserve the fallopian tube. Sometimes the fallopian tube has to be removed. If the doctor does not remove the fallopian tube, a new pregnancy can lead to another ectopic pregnancy.
Egg remnants can sometimes remain in the fallopian tube, so there is a risk that they will degenerate over time. For this reason, once the woman has completed her family planning, the medical professionals decide to have the fallopian tube removed. If there is an ovarian pregnancy, the doctor tries to remove the fruit from the ovary; in a few cases, however, the ovary must be completely removed.
If there is a cervical pregnancy, i.e. implantation in the cervix, the doctor must remove the uterus. Chooses the physician for a medication he prescribed methotrexate (MTX, a so-called cell poison that even with cancer – or rheumatism treatments will be applied), dinoprostone, prostaglandins, hyperosmolar glucose and Antigestagens such as mifepristone.
The combination leads to the death and also to the shedding of the fruit, which then migrates into the abdomen. MTX is given to an ectopic pregnancy that has no complications; sometimes MTX can also be given after the operation to kill any egg cell debris.
Beta-HCG, the pregnancy hormone, can be used to determine whether the medication has the desired effect in the end. The drugs are only given via muscle injections or blood infusions; The active ingredients are only rarely administered in tablet form.
Outlook & forecast
In most cases, an ectopic pregnancy ends in an abortion. Only a few cases of ectopic pregnancy are known in which a viable child could develop outside the uterus. These rare pregnancies had to be terminated by a incision birth.
As a rule, however, ectopic pregnancy triggers the first symptoms after days or weeks, including severe abdominal pain, fever, fatigue and the absence of a menstrual period. If the woman is not treated now, toxins are distributed in the body and inflammation of the surrounding internal organs can occur with serious complications up to and including organ failure.
If an ectopic pregnancy is recognized in good time and is surgically terminated by the gynecologist, the woman only needs a short recovery phase and can then go home. The procedure can be compared to an abortion. She can get pregnant again a short time afterwards, as long as there were no infrequent injuries during the procedure.
However, the longer an ectopic pregnancy persists without treatment, the higher the risk of irreversible damage to the fallopian tubes and uterus, so that a new pregnancy may be difficult or impossible in individual cases. A patient also needs more time to recover after an emergency operation because of an ectopic pregnancy and has to be monitored in the hospital to rule out complications and consequential damage.
Prevention
Ectopic pregnancy can hardly be prevented. If the woman has an inflammation of the fallopian tubes, it is important to treat the disease as quickly as possible so that there is no damage that can lead to ectopic pregnancy.
Aftercare
In the case of an ectopic pregnancy, the options for follow-up care are very limited in most cases. First and foremost, the patient depends on medical treatment for the disease in order to prevent further complications and complaints. It cannot heal on its own, so treatment of the extrauterine pregnancy by a doctor is essential.
In most cases, this disease is treated with a surgical procedure, which has no particular complications. After the procedure, the patient should always rest and take care of his body. You should refrain from strenuous activities or other complaints in order to speed up the healing process. Even after successful treatment, regular examinations of the body should be carried out, as ectopic pregnancy can also promote the formation of tumors.
A doctor must also be consulted to prevent the tumor from spreading. Those affected are still dependent on intensive care and support from their own family and friends so that there is no psychological upset or depression. Contact with other people affected by the ectopic pregnancy can also be useful.
You can do that yourself
In the case of pregnancy, the woman cannot influence whether the fertilized egg is normally implanted in the uterus or outside in the fallopian tube. In everyday life, however, there are a number of ways that women can use self-help to influence the ectopic pregnancy in a positive way, both in terms of the acute course and the subsequent regeneration.
First of all, in the course of an early pregnancy, it is necessary for a woman to have the correct fit of the pregnancy confirmed by the attending gynecologist as quickly as possible by means of an appropriate ultrasound examination. This offers protection especially in those cases in which there are unusual symptoms or the woman has already had an ectopic pregnancy. Because the earlier the ectopic pregnancy is treated, the fewer complications there are, and the faster the regeneration.
After the ectopic pregnancy therapy, the affected woman can contribute to improving her physical and mental condition in everyday life. In the physical area, according to medical advice, these are protection and avoidance of baths. In the psychological area, empathetic conversations with people they trust help women to come to terms with the loss of pregnancy. After physical regeneration has taken place, exercise and yoga often stabilize the mental state.