As exogenous allergic alveolitis, inflammation of the alveoli is called. It is created by inhaling fine dust.
What is exogenous allergic alveolitis?
According to definitionexplorer.com, exogenous allergic alveolitis (EAA) or exogenous allergic alveolitis is an inflammation of the aleveoli that is allergic. The alveoli are alveoli that are affected by the inhalation of fine dust. These can be chemical substances or organic dust.
If the harmful substance is inhaled as part of an occupational activity, exogenous allergic alveolitis can be classified as an occupational disease. In Germany, around 5 to 15 percent of the population is affected by an EAA. The inflammation of the alveoli is most common in pigeon breeders and farmers.
Causes
The cause of exogenous allergic alveolitis is repeated inhalation of organic dust. If this gets into the lungs, an allergic overreaction occurs in the body. Type III and IV immune reactions are of particular importance. The immune complexes cause the complement system to become active. In addition, messenger substances are formed with inflammatory cells. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes result in the development of granulomas within the alveolar space.
Acute pneumonitis develops depending on the extent of the allergen exposure and how long it lasts. There is also a risk of developing pulmonary fibrosis due to smaller pneumonitic attacks. In exogenous allergic alveolitis, the risk of disease is different. Atopic people are particularly at increased risk. Various antigens are responsible for exogenous allergic alveolitis and trigger an overreaction in the body.
The approximately 300 known antigens include chemicals, animal proteins, bacteria as well as fungi and fungal spores. It is not uncommon for the EAA to be related to the patient’s professional activity. One form of exogenous allergic alveolitis is the avian lung. It is caused by bird feathers or bird droppings. Another variant is the farmer’s lung, which is caused by mold spores in grain or hay.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
Exogenous allergic alveolitis can be divided into an acute and a chronic form. The acute form sets in about 4 to 12 hours after the patient breathes in the trigger. This leads to symptoms such as dry cough, shortness of breath when resting, headache, chills and high fever.
In addition, those affected feel a general feeling of illness. The chronic EAA usually manifests itself as a gradual decrease in performance, loss of appetite, fatigue and weight loss. When exerted, patients increasingly suffer from difficulty breathing and coughing.
The acute form of exogenous allergic alveolitis usually results from a massive supply of antigens. This includes cleaning a dovecote or moving moldy hay. Symptoms are similar to those of an infectious disease, but they are not caused by an infection. The acute EAA often heals on its own after a few days. The chronic form of EAA is difficult to discover. Over time, it leads to the destruction of the lung tissue, also known as pulmonary fibrosis.
Diagnosis & course
Exogenous allergic alveolitis cannot be diagnosed with just one finding. For this reason, the diagnosis consists of the exclusion of other diseases. Different diagnostic methods are also used. The symptoms of the disease also play an important role.
During the physical examination, the doctor often notices a crackling rattle while listening. An x-ray examination can sometimes reveal a milky, glassy cloudiness. However, it does not occur in around a third of all patients. If the form is chronic, increasing scarring can be determined, but this also shows up in other lung diseases.
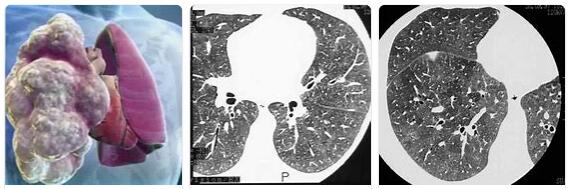
Exogenous allergic alveolitis can be reliably proven by high-resolution computed tomography (HR-CT). Even early forms that go undetected on the X-ray can be diagnosed with their help. A blood test enables the detection of special antibodies against the causer.
It is not uncommon for the EAA to be recognized late. This can result in delayed treatment of the patient, which in turn creates the risk of pulmonary fibrosis. As a result, the fibrosis only regresses slowly or not at all. However, if treatment is timely, the course of the disease is usually positive.
Complications
The exogenous allergic alveolitis belongs to a group of immunologically caused lung diseases. Inhaling various types of organic dust can cause an inflammatory reaction in the lungs, bronchi and airways. Especially in the area of animal husbandry and rooms operated in air conditioning systems, the symptom is more work-related.
Sometimes the disease is misinterpreted, as the signs and course forms often express themselves as a flu-like effect. However, a blood count clearly shows leukocytosis, which requires a thorough medical anamnesis. After considering the professional and private background of the patient, among other things, exogenous allergic alveolitis can be suspected.
If the typical crackling rattle cannot be heard when listening to the lungs, imaging procedures and holistic diagnostics can confirm the findings. If the symptom is delayed, complications inevitably occur, which affect the person concerned professionally and life-impairing. In addition to recurring attacks of fever, persistent cough, a permanent feeling of flu and exhaustion, exogenous allergic alveolitis can take on chronic proportions.
The consequences are shortness of breath, inexplicable weight loss, watch glass nails, drumstick fingers and chronically progressive pulmonary fibrosis. If the fibrosis has started with scarring of the pulmonary areas, it can hardly be healed. If the symptom is recognized in good time, glucocorticoids are used to enable allergen avoidance.
When should you go to the doctor?
This condition should be evaluated by a doctor. Although it does not have to lead to complications or serious complaints immediately, it can, in the long term, damage the internal organs. The person concerned should then consult a doctor if he suffers from severe shortness of breath or from a dry cough. This can also occur with bloody sputum.
If the patient loses consciousness due to the illness, an emergency doctor must be called immediately and mouth-to-mouth resuscitation carried out. A stable side position can also save the patient. Treatment should also be initiated if the person has a high fever or headache and chills.
Persistent tiredness or loss of appetite can also be symptoms of the disease. The difficulty breathing and cough usually increase and worsen over time. The first diagnosis and treatment can be given by a general practitioner or an ENT specialist. The earlier the diagnosis is made, the higher the probability of a positive course of the disease. Further treatment, however, depends on the severity of the symptoms and possibly also on the damage to the internal organs.
Treatment & Therapy
In order to successfully treat exogenous allergic alveolitis, the affected person must absolutely avoid the triggering allergen. Effective treatment cannot be carried out without consistent allergen avoidance. For the therapy, the doctor determines whether there may be an occupational disease. If the patient avoids the triggering allergen, the symptoms usually go away after a few days.
The patient is given high doses of glucocorticoids so that the inflammatory reaction is successfully combated in an acute EAA. Some sufferers also have a superinfection that also requires medical therapy. If the patient suffers from chronic exogenous allergic alveolitis, he is given highly potent immunosuppressants. These agents can reduce pulmonary fibrosis.
If the fibrosis is more advanced, however, there is a risk of serious complications such as right heart failure or pulmonary hypertension. If the patient’s condition continues to deteriorate, treatment options such as long-term oxygen therapy or a lung transplant may be considered.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis of exogenous allergic alveolitis is favorable if certain guidelines are observed. If the inhalation of fine dust is avoided, there is no symptom. Although the disease cannot be cured, the person affected can still achieve relief by regulating their behavior. The area must be cleaned of dust at regular, close-knit intervals. If the cleaning succeeds to a sufficient extent, no further inconvenience occurs. For this, the professional as well as the private premises have to be optimized.
In severe cases, exogenous allergic alveolitis takes an unfavorable course. It can lead to a disturbance of the cardiovascular system. In some patients, the heart’s function is so weakened that serious and life-threatening complications occur. Long-term therapy is necessary to avoid the patient’s premature death.
If the pollution of the fine dust persists during inhalation, organ damage can also develop. Damage to the lungs can lead to permanent breathing disorders and shortage of breath. Artificial ventilation secures the life of the person affected. An organ transplant is indicated in these cases to enable an improvement in health. The surgical procedure is associated with numerous risks and side effects. If the donor organ is not accepted by the organism, the patient is at risk of death.
Prevention
The best preventive measure against the EAA is the consistent avoidance of the triggering allergen. For example, patients who suffer from avian lungs must not have any contact with ornamental birds or other bird species.
Aftercare
As a rule, there are no special measures or options for follow-up care available to those affected by this disease. The patient is primarily dependent on a quick and, above all, an early diagnosis. This is the only way to prevent further complications and complaints. Without treatment for this disease, the symptoms will usually worsen, so treatment by a doctor is essential.
With this disease, the person affected is primarily dependent on taking medication. It is important to ensure the correct dosage with regular intake in order to permanently alleviate the symptoms. If there are any questions or uncertainties, the person concerned should always contact a doctor first.
Furthermore, the person concerned should not strain his body unnecessarily and avoid strenuous exertion in order not to strain the heart. Help and care from your own family or friends are also very important. Psychological care is also very important in order to prevent psychological upsets or depression. This disease can also reduce the life expectancy of those affected.
You can do that yourself
Acute exogenous allergic alveolitis usually shows up a few hours after inhaling the allergen. If the patient avoids the allergenic substances, the symptoms usually go away on their own after a few days. The best self-help measure, therefore, is to identify the allergens and avoid contact.
It’s not always easy. If there is no suspicion of the trigger, the person affected should keep an allergy diary. It records in detail what the patient is doing and what symptoms are observed and when. Such a diary can support the attending physician in carrying out specific allergy tests.
If the patient has an allergic reaction to a substance that he regularly has to deal with professionally, he usually has to give up his job and look for another occupation. Retraining is often required. Since exogenous allergic alveolitis is often classified as an occupational disease in these cases, patients are relatively well covered.
In any case, those affected should seek advice in good time either from their trade union, from their works council or from a specialist lawyer for social law in order to keep the financial consequences of the illness as low as possible.