The Fallot tetralogy (Fallot tetralogy) is a congenital heart defect which, due to its various individual diseases, is highly complex and also often occurs in newborns. The defect in the heart septum was named after the French Dr. Étienne-Louis Arthur Fallot, who first reported on this disease in 1888.
What is a Fallot tetralogy?
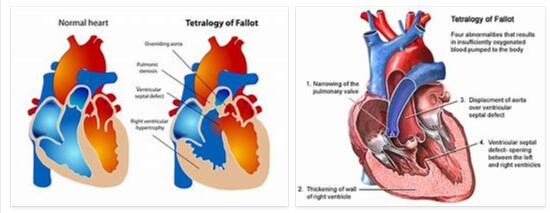
According to whicheverhealth.com, the Fallot tetralogy is made up of four (tetralogy) individual diseases that occur at the same time. Disease No. 1 is what is known as pulmonary stenosis (narrowing of the pulmonary artery). No. 2 of the Fallot tetralogy is the heart wall defect, which creates a continuous connection between the two heart chambers.
The third individual disease in Fallot’s tetralogy is an enlargement of the heart muscle in the area of the right ventricle. Single disease no. 4 is a malalignment of the main artery (aorta).
Due to the defect in the heart septum, oxygen-rich blood mixes with oxygen-poor blood, which leads to cyanosis. This condition is commonly referred to as “blue baby”, because the insufficient supply of oxygen causes the skin and the mucous membrane to turn bluish. The Fallot tetralogy is one of the most common heart defects in newborns.
Causes
A cause for the Fallot tetralogy is not known. Previous assumptions most likely see a genetic disposition, i.e. a genetic defect or a hereditary disease. Studies have shown that affected children often have a defective set of chromosomes, as occurs, for example, in Down syndrome.
A so-called chromosome deletion 22q11 is found here, an error in the DNA that can be detected in around 15 percent of the sick. Those affected suffer from shortness of breath, among other things, as the lungs are not supplied with sufficient blood due to the defect in the heart wall and pulmonary stenosis. The causes of the complaints can be assigned to the four individual diseases of the Fallot tetralogy.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
In the Fallot tetralogy, those affected suffer from a congenital heart defect. As a rule, this mistake can have very different effects on the life of the person affected and lead to various complaints or complications. The patients often suffer from a blue discoloration of the skin or the mucous membranes.
If the body continues to be undersupplied with oxygen, this can also lead to a loss of consciousness and, in the worst case, damage to the internal organs or the brain. This damage is irreversible and can no longer be treated. Furthermore, the Fallot tetralogy also leads to loud heart noises and permanent tiredness or fatigue in the patient.
This also significantly limits the child’s development, as the child cannot participate in strenuous or sporting activities. The disease can also lead to permanent high blood pressure, which has a very negative effect on the health of the person affected and can possibly also reduce life expectancy.
If the disease is left untreated, it can also lead to sudden cardiac death. Due to the symptoms of the disease, some people also suffer from psychological limitations or depression and are therefore dependent on psychological treatment.
Diagnosis & course
The diagnosis of Fallot tetralogy is made by the cardiologist. Since the heart defect makes itself felt at the beginning with the symptom of the “blue baby”, the conversation with the parents is an important indicator for the diagnosis.
Physical examinations will then be carried out. This is followed by laboratory diagnostics and the use of imaging methods such as X-rays, MRT (magnetic resonance imaging) and ultrasound. An EKG (electrocardiogram) provides information about the heart’s activity.
If these examinations confirm the Va to Fallot tetralogy, the entire blood supply to the lungs and heart is then examined by means of a cardiac catheter examination as well as a so-called angiography. If Fallot tetralogy is suspected, special attention is paid to the coronary arteries as well as the pulmonary artery.
The course of the Fallot tetralogy depends above all on the blood flow to the lungs, as it ensures the oxygen supply to the body. If the Fallot tetralogy is treated in good time, those affected have a good life expectancy. After the operation, there may be occasional cardiac arrhythmias and an increased tendency to high blood pressure in the blood vessels of the lungs. If these complaints do not subside and the heart function deteriorates as a result, further surgery is usually unavoidable.
The mortality rate with surgical therapy is less than three percent (when treating children). In adults, the mortality rate is around nine percent. Current studies and examinations of those affected have shown that 90 percent of people with Fallot tetralogy lived at least 30 years after the operation, around 75 percent of those affected lived at least 40 years after successful treatment. The long-term prognosis for the Fallot tetralogy can be classified as good to very good.
Complications
Due to the Fallot tetralogy, various complications can usually arise, most of which affect the heart of the newborn. In many cases, unusual heart murmurs occur which can lead to a panic attack in many patients. The affected person’s skin also often turns blue, which leads to what is known as cyanosis.
Complications can arise when the organs are no longer supplied with sufficient oxygen. In the worst case scenario, irreversible damage to certain organs occurs. The cardiac arrhythmias can be treated with surgical interventions. In most cases, the operation on the heart proceeds without complications and the symptoms of the tetralogy of Fallot can be severely limited.
Complications will continue to arise if treatment is not given in the first year. In this case, life expectancy is reduced even further by the Fallot tetralogy. Due to the heart defect, the patients can no longer do sports as usual and are severely restricted in their everyday life.
When should you go to the doctor?
The Fallot tetralogy must always be treated by a doctor. If the disease is not treated, it can, in the worst case, lead to the death of the patient. A doctor examination is necessary if the person concerned has breathing difficulties and continues to have blue skin. This can also lead to a loss of consciousness in the patient. In this case, an emergency doctor must be called. Until the emergency doctor arrives, calm breathing and a stable lateral position of the patient should be ensured.
In emergencies, the affected person should be ventilated. A visit to the doctor is also necessary if the patient suffers from loud heart noises or pain in the area of the heart. Persistent tiredness or fatigue can also indicate the disease and should be examined if the symptoms occur over a long period of time.
Usually, Fallot tetralogy can be diagnosed by an internist or cardiologist. The treatment itself then takes the form of a surgical procedure. In most cases, early detection and successful treatment will not affect the patient’s life expectancy.
Treatment & Therapy
The Fallot tetralogy is usually treated with a surgical intervention. The earlier the operation, the better the chances of recovery. Studies have shown that the procedure should be carried out within the first year of life.
Treating the Fallot tetralogy involves several steps. In the case of newborns as well as infants, a so-called balloon dilatation is carried out at the beginning. The attempt is made to expand the narrowed heart valve, which lies between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery. This ensures an improvement in blood flow, which leads to higher oxygen saturation in the blood.
Since the Fallot tetralogy consists of four individual diseases, all four diseases must be treated during the operation. In addition to the aforementioned expansion, defects in the heart septum are closed. The misalignment of the aorta is corrected and the enlargement of the heart muscle in the area of the heart chamber is assessed and, if necessary, corrected. The surgical treatment of the Fallot tetralogy is now one of the routine interventions.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis for a congenital Fallot tetralogy is relatively good thanks to today’s medical knowledge. That was not always so. This complex heart disease, the consequences of which are serious, can now be treated surgically.
In order to ensure the greatest possible success of the operation, it is important that the operation is carried out in the first year of life. If the procedure is successful, the chances of survival for those affected are at least 90 percent after 30 years. Around three quarters of the babies who have been operated on will still be forty years of age. However, this also means that for a quarter of those operated on with Fallot’s tetralogy there was no further chance of survival.
Since Fallot’s tetralogy accounts for around ten percent of all congenital heart defects, the surgical procedures that are successfully used today have been refined over the course of time. This has improved the prospects for longer survival considerably. Even so, the disease is so complex that some of the children affected do not survive the operation.
If adults are operated on with a Fallot tetralogy, the postoperative death rate is higher. The prognosis is made dependent on the blood flow in the lungs. In some cases, two surgical interventions are necessary. As a postoperative complication, the formation of scar tissue in the heart region can lead to cardiac arrhythmias even after years. Lifelong medical monitoring is indispensable for those affected with Fallotian tetralogy.
Prevention
Since the cause of the Fallot tetralogy is largely unknown and is probably due to a genetic defect, preventive measures can only be taken to a limited extent. Pregnant women can take advantage of what is known as genetic counseling during the general examinations. There is also the so-called prenatal diagnosis, during which a heart defect can be detected using ultrasound, among other things.
If there are Fallot tetralogies in the family, pregnant women should choose a clinic for childbirth that has a cardiology department for children. There is currently the so-called maternal hyperoxygenation study, in which it is checked whether a targeted oxygen therapy can prevent the Fallot tetralogy during pregnancy.
Aftercare
In the case of the Fallot tetralogy, in most cases there are no special follow-up options available to the patient. Those affected are primarily dependent on the treatment of the heart defect in order to prevent further complications and premature death. Self-healing cannot occur, although an early diagnosis with early treatment can have a positive effect on the further course.
The Fallot tetralogy is usually treated with a surgical procedure. This usually proceeds without complications and leads to a significant improvement in the symptoms. After the procedure, the person concerned should rest and take care of the body.
In doing so, strenuous, stressful or sporting activities should be avoided in order not to unnecessarily burden the heart and circulation. Furthermore, regular check-ups and examinations by a doctor to monitor the heart are useful even after a successful operation.
Further options for follow-up care are not available to the person concerned and are usually not necessary with the Fallot tetralogy. In general, a healthy lifestyle with a healthy diet also has a positive effect on the course of this disease. After the successful operation, the body can again be stressed as usual.
You can do that yourself
The possibilities for self-help are very limited in the Fallot tetralogy. The surgical intervention represents the best chance of success for a cure. Therefore, the guidelines of the medical practitioner must be followed. In order to alleviate the physical complaints, overexertion should also be avoided and the general stress should be kept low.
As soon as heart problems occur or blood pressure rises, keep calm and take a break. The weight should be within the normal range according to the guidelines of the BMI and obesity should be avoided. A healthy diet and regular exercise stabilize the immune system and help build up the body’s defenses. As a general rule, you should refrain from spending any kind of money.
Relaxation procedures are helpful for mental relief. They strengthen the psyche and reduce stress. With yoga, meditation or other relaxation exercises, inner balance can be achieved and new mental strength can be built up. With an optimistic basic attitude, the well-being is also improved and the chances of recovery increase.
If blood flow disorders are noticed, immediate action should be taken. Targeted movements of the hands, fingers, feet or toes prevent exposure to cold due to insufficient blood circulation. Physical activity should be minimized if heart palpitations occur. Sufficient sleep and regular interruptions to everyday activities improve the existing state of health.