The FG syndrome is an X-linked abnormality. Those affected suffer from defective vitamin D receptors and, as a result, from complex symptoms such as developmental delay, muscle weakness, strabismus and inner ear hearing loss. Treatment is symptomatic.
What is FG Syndrome?
According to ezhoushan.net, chromosomal aberrations are also known as chromosomal abnormalities. These are structural or numerical changes in chromosomes in an organism or a specific cell. Chromosome aberrations are therefore major changes within the genome that can trigger serious clinical pictures.
A structural chromosomal abnormality is the FG syndrome, which is also referred to in the literature as Opitz-Kaveggia syndrome or Keller syndrome. The disease is a serious and rare condition caused by abnormalities in the X chromosome that, in addition to physical abnormalities, results in developmental delays.
The disease was first described in 1974. John Marius Opitz and Elisabeth Kaveggia are considered to be the first descriptors. The name FG syndrome has its roots in an acute case of the syndrome. The letters F and G are the initials of the surnames of two sisters who gave birth to several children with the syndrome.
According to current knowledge, there are allelic connections between FG syndrome and Lujan-Fryns syndrome. The prevalence for FG syndrome is estimated at one case in 500 newborns. Also, heart defects and defects of the limbs are not excluded.
Causes
FG syndrome is caused by mutations in the MED12 gene, better known as mediator complex subunit 12. The gene is located on gene locus 13.1 of the X chromosome and carries 44 exons. The unit codes in the DNA for a subunit of the mediator complex, which is also known as the mediator or thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein.
Other names are TRAP or thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein, vitamin D receptor interacting protein, and DRIP and vitamin D receptor interacting protein. The protein-rich gene product consists of 28 subunits.
If there is a structural abnormality in the corresponding chromosome, the structure of the protein changes so that the complex no longer fulfills its physiologically intended functions and a defective vitamin D receptor is formed.
There are different sub-forms of the FG syndrome, which depend on the exact gene locus of the chromosomal abnormality. In addition to the Xq13 locus, anomalies have been documented in FLNA Xq28, Xp22.3, CASK Xp11.4-p11.3 and Xq22.3. Due to the family disposition observed, an x-linked hereditary basis is suggested.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
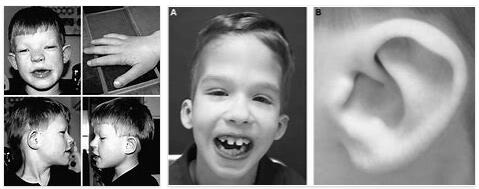
Patients with FG syndrome show symptoms of mental retardation. In most cases, there are also multiple personality changes. A strong tendency to hyperactivity was observed in almost all cases. Concomitant symptoms may be abnormalities in the area of the face.
The facial features of the patients, for example, often appear inanimate and unfriendly. In many cases, there is low muscle tone throughout the body. The corners of the mouth hang down accordingly and motor skills can be restricted. In some cases a permanently open mouth was observed, which is also due to the reduced muscle tone. Digestive tract symptoms were also documented.
Chronic constipation is one of the most important symptoms in this context. In individual cases, foramen parietal permagnum (FPP) was found in the patient. It is a rare disorder of skull development that is associated with bone defects in the parietal bone and significant enlargement of the parietal foramina.
The respiratory tract of many patients is also susceptible to infections. In addition, cleft palate, larynx, strabismus, hernias, hypospadias, hydroceles, sleep apnea and inner ear hearing loss as well as recurrent otitis or reflux can be signs of the FG syndrome.
Diagnosis & course
The first suspected diagnosis of FG syndrome is made in infancy or early childhood. Clinical symptoms such as decreased muscle tone, the permanently open mouth and chronic constipation are usually the first indications of the syndrome. The doctor provides evidence of the reduced muscle tone through neuroelectrical examinations.
Molecular genetic methods are used to confirm the diagnosis, which provide evidence of the causative chromosomal abnormality. Slight variants of the GBBB syndrome, the Atkin-Flaitz syndrome, the fragile X syndrome and the Keipert syndrome, the naso-digito-acoustic syndrome and the Say-Meyer syndrome are to be distinguished from the differential diagnosis.
The same is true for Donnai-Barrow syndrome, Sotos syndrome, and C syndrome. The Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, the Dubowitz syndrome and Renpenning syndrome are possible differential diagnoses. A suspicion can be raised prenatally in the malformation ultrasound. The prognosis for patients with FG syndrome is poor. Many of those affected die in childhood. Few of the patients die after the critical phase of childhood.
When should you go to the doctor?
Parents who notice malformations, signs of chronic constipation, and other indications of FG syndrome in their child should see their pediatrician. The X-linked abnormality is a serious condition that definitely needs to be diagnosed and treated. Therefore, unusual complaints, external abnormalities and other symptoms should be clarified by a doctor. If serious complications arise, the best case scenario is to contact the emergency medical service or the child should be brought to a hospital immediately.
Patients with FG syndrome should be closely monitored and examined regularly. Treatment may need to be carried out by more than one doctor, depending on the severity of the abnormality. In the case of hearing problems, an audiologist must be called in, while in the case of visual disturbances, the ophthalmologist or optician is the right contact. The doctor in charge can best answer the precise question of which medical professionals need to be involved. In most cases, he will also recommend therapeutic advice to the parents and initiate the necessary support for the child.
Treatment & Therapy
A causal treatment for the FG syndrome is not yet available. Because it is a genetic disease, advances in gene therapy over the next few decades may open up causal treatment options. At the present time, patients with the syndrome are treated symptomatically.
The therapy of the life-threatening symptoms is the focus of the treatment measures. Above all, possible heart defects must be corrected invasively. Surgical treatments are also available for cleft palate, larynx, reflux, hernia, squint, hypospadias, and hydrocele.
A feeding tube may be required to maintain the nutritional situation. CPAP ventilation is used for sleep apnea. Inner ear hearing loss is treated with cochlear implants. Doctors counter relapsing otitis with tubes to equalize pressure.
Therapy with growth hormones can counteract severe growth disorders. On the supportive therapeutic side, parents of affected children receive psychological support. Mental retardation is counteracted therapeutically by means of early support.
Outlook & forecast
The FG syndrome offers an unfavorable prognosis. The sick children often die during childhood. If the first years of life are survived, there is a high chance of survival. However, the symptoms significantly impair the patient’s well-being and general quality of life. Therefore, psychological treatment must always be initiated during therapy. This can at least improve mental well-being.
Nevertheless, the FG syndrome is a serious disease that puts a great deal of stress on those affected. Mental retardation in particular has a negative impact on health, as it is associated with numerous neurological complaints. Concomitant symptoms such as constipation or parietal permagnum foramen can lead to further complications in the course of life, from which the patient may die.
Life expectancy is reduced and most of the sick die either in childhood or between the ages of 40 and 50. The restricted mobility can cause bed rest, obesity and many other secondary complaints and long-term consequences, which mean a further deterioration in the health of those affected. Early therapy can alleviate symptoms and enable patients to lead a relatively normal life in a care facility.
Prevention
So far, the FG syndrome can only be prevented through genetic counseling in family planning and, if necessary, fine ultrasound during pregnancy. If you have a family history, the decision against having your own child is considered the most effective and so far the only preventive measure.
Aftercare
In most cases, the follow-up options for FG syndrome are severely limited. Since this is a genetically determined disease, it cannot be treated completely or causally. In order to prevent the inheritance of the FG syndrome to the children, genetic counseling should be carried out if the child wishes to have children. Self-healing cannot occur with this disease.
Most of those affected are dependent on surgical interventions to alleviate the symptoms. The patient should take it easy after such an operation and not engage in physical activity. In general, you should refrain from physical exertion or other stressful activities.
Furthermore, those affected are often dependent on the intake of hormones that are supposed to promote the patient’s growth. Care must be taken to ensure that these hormones are taken correctly and, above all, regularly, and possible side effects or interactions must also be taken into account.
A doctor should therefore always be consulted if anything is unclear. Parents must ensure that their children are taking the medication correctly, especially when it comes to their children. Since the FG syndrome can often lead to psychological complaints in parents or relatives, they should also consult a psychologist.
You can do that yourself
The possibilities for self-help with FG syndrome are limited. Those affected depend on treatment by a doctor to limit the symptoms.
As the children suffer from increased retardation, they need strong support and encouragement in their lives. Above all, this must be done by one’s own parents and relatives. This can minimize further complications in adulthood. Hyperactivity can also be treated with special training.
Since many patients also suffer from visual problems, visual aids should be worn from a young age. This can prevent further deterioration in eyesight. Reflux disease should also be diagnosed and treated at an early stage in order to avoid a possible ulcer or tumor disease.
However, parents often also need psychological support. This can take place through a psychologist or through discussions with other affected persons. Regular consumption of growth hormones can also reduce growth and development disorders. The FG syndrome cannot be prevented directly. However, prenatal examinations can indicate the syndrome early on.