Heart valves act as a kind of valve in the heart engine: they ensure that the blood always flows in the right direction and does not go back to where it just came from. A heart valve defect prevents this functioning and can have fatal consequences. Subtypes of heart valve defects are heart valve insufficiency or heart valve weakness.
What is a heart valve defect?
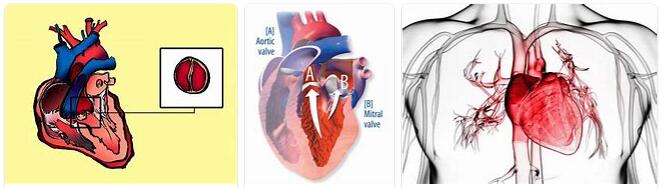
According to abbreviationfinder.org, the human heart has a total of four heart valves: The aortic and mitral valves are the most frequently affected by heart valve defects.
A heart valve defect is a functional disorder of the heart that is either congenital or – for example through an illness – can be acquired. There are different types of heart valve defects: The so-called stenosis is a narrowing of the heart valve that prevents blood from flowing through.
In the event of an insufficiency, the heart valve only closes incompletely, so that blood can flow back. If the doctor speaks of a combined vitium, he means a combination of the first two heart valve defects.
Causes
A heart valve defect is congenital in most cases. Sometimes, however, one can also acquire one, for example through an illness. There are a variety of diseases that can result in heart valve defects. This also includes an uncured flu. It is therefore essential to ensure that you refrain from endurance training if you have influenza, but also only if you have a severe cold, and instead take it easy.
If you go jogging with a bad cold, this can lead to a dramatic undersupply of oxygen to the blood, even in young, well-trained people. As a result, the heart has to pump harder and can become so overloaded due to illness that one or more heart valves no longer close properly.
In other cases, the heart valves degenerate primarily due to age: with increasing age, not only the blood vessels but also the heart valves calcify. This process usually results in a narrowing of the heart valves. Another common cause of heart valve defects is inflammation of the same caused by bacteria, for example.
Symptoms, Ailments & Signs
The symptoms differ significantly according to the severity, location and type of heart valve defect. Many heart valve defects go unnoticed for a long time because they initially do not cause any symptoms. However, in some cases, such as mitral valve stenosis, very clear symptoms can also occur acutely. In principle, the heart can compensate for most valve defects over a long period of time.
However, this leads to cardiac insufficiency (cardiac insufficiency) in the longer term. In some cases, heart valve defects are not noticed until then. A typical symptom is a feeling of tightness and strong pressure in the chest area. This is especially the case with physical exertion. In addition, many of those affected suffer from rapid fatigue and general exhaustion.
Your performance and concentration can decrease significantly. Dizziness and brief fainting spells (syncope) are common . Which symptoms actually occur also depends on whether the heart valve defect affects the left or right ventricle. Valve defects in the left ventricle cause symptoms that can resemble those of bronchitis.
These include shortness of breath and a strong urge to cough (especially at night). Those affected feel more comfortable in an upright position than lying down. Cardiac arrhythmias often occur in the long term. If the right heart valve is affected, water retention in the legs and abdomen, blue discoloration of the skin, shortness of breath and liver pain occur.
Diagnosis & History
Mild heart valve defects are usually discovered by accident and usually do not require treatment. Most of the time they are symptom-free. However, typical signs of severe heart valve defects can be shortness of breath, a feeling of tightness in the chest, but also high blood pressure.
Sometimes there may be fainting spells. Heart valve defects are diagnosed using an ECG and ultrasound. During an ultrasound, the cardiologist (ie a doctor who specializes in the human heart) examines the blood streams and checks whether they are flowing as desired. The ECG (also known as an electrocardiogram or heart chart) is carried out either as a 24-hour ECG or a stress ECG.
In the case of a 24-hour ECG, the patient has 4 electrodes glued to the skin, which are connected to a small box about the size of a walkman. The box fastens at the waist. The ECG then measures the heart’s activities during a normal daily routine. Another indication of a heart valve defect are cardiac arrhythmias and suspicious noises.
Complications
The heart valve defect can lead to heart failure and thus to the death of the patient. As a rule, life expectancy is significantly reduced by the heart valve defect if this disease is not treated. The person affected suffers from severe high blood pressure as a result of the error and thus also from an increased risk of a heart attack.
Furthermore, stress can lead to shortness of breath and thus to sweating or panic attacks. The general resilience of the patient drops enormously and cardiac arrhythmias develop. These have a very negative effect on the everyday life of the patient and lead to a reduced quality of life. In some cases, patients lose consciousness completely or may die from shortness of breath.
It is also not uncommon for mental disorders or depression to occur. The heart valve defect can only be eliminated with the help of a surgical intervention. An artificial valve is used, which usually does not lead to any particular complications. In severe cases, inflammation can occur after the operation. Therefore, for prevention, the patient must also take antibiotics to prevent these inflammations. If the treatment is successful, there is no reduction in life expectancy.
When should you go to the doctor?
If symptoms such as shortness of breath, high blood pressure or a drop in performance are noticed, there may be a heart valve defect. A visit to the doctor is recommended if the symptoms persist for a longer period of time. If there are other symptoms, such as signs of heart failure or a general decrease in well-being, medical advice is also required. In the event of disturbances of consciousness and fainting spells, the best thing to do is call an ambulance or take the person concerned to the nearest hospital immediately.
The same applies to acute heart pain and severe shortness of breath. If there is a suspicion of cardiac arrhythmia, this must also be clarified by a doctor and treated if necessary. Elderly people and people who may not have recovered well from the flu are particularly at risk of developing a heart defect. Viral infections, tumor diseases and other diseases can also cause heart valve defects. Anyone who belongs to this risk group should speak to their family doctor if they experience the symptoms mentioned. Further treatment is usually carried out by a cardiologist or an internist. In most cases, therapeutic advice is also useful, since a heart valve defect can be a significant burden on the psyche.
Treatment & Therapy
A heart valve defect cannot be eliminated by the administration of medication. An operation is usually necessary. Sometimes your own diseased valve can be reconstructed, but in the case of serious heart valve defects, the damaged heart valve is replaced.
Instead, the patient receives an artificial valve. If a heart valve has become too narrow, for example due to calcification, it can also be stretched using what is known as dilatation. This is done with the help of a balloon, which is folded up and placed in the appropriate place and then gradually expanded.
However, this procedure is only possible in rare cases. In the case of heart valve patients, any bacterial infection can be dangerous, as it can lead to an inflammation of the heart. For this reason, antibiotics are often given as a preventive measure.
Outlook & Forecast
The prognosis of heart valve defects depends on the affected heart valve and the progression of the disease. A potentially poor prognosis exists when the patient’s cardiac function is compromised. If there is a major heart valve defect, there is also an increased risk of an unfavorable course of the disease. Surgery is necessary to ensure the patient’s survival.
If the operation is successful, the patient can lead a good life despite the disease. Nevertheless, the quality of life is limited and secondary diseases are possible. These are mostly from the psychotherapeutic field, since an inevitable change in the current way of life and restriction of the usual possibilities for health reasons leads to mental suffering in many people.
A small or mild heart valve defect is treated with medication in most cases. Lifestyle must also be restricted and changed to prevent life-threatening health conditions.
In principle, patients with a heart valve defect must undergo regular medical check-ups, as cardiac activity can deteriorate at any time. There is a lifelong possibility that the symptoms will increase and the heart will fail to function properly. If left untreated, the patient with a heart valve defect is at risk of premature death. The cardiac activity is disturbed and can bring about a sudden, acute condition that is dangerous to health.
Prevention
If you want to prevent a heart valve defect, you should change your diet: Lots of fruit and vegetables, but little fat and meat ensure good heart health. A normal blood pressure (120 to 80 is optimal) and avoiding obesity also contribute to health. Lots of exercise in the fresh air helps. However, if you are ill, you should avoid exercising. Bed rest is urgently needed here. Often, however, an infection by bacteria can result in a heart valve defect. Above all , streptococci are dangerous to humans.
Aftercare
Medical support after heart valve surgery is essential. A stay in the hospital is usually followed by a cure. Since the patient must take anticoagulant medication, regular check-ups should be carried out. In the case of biovalves, this is necessary for a period of three to six months; in the case of artificial valves, these medications are intended to be taken for life.
It is important for those affected to test or observe themselves after an operation and to see their doctor immediately if their body gives any warning signals. A blood count is used to determine any inflammation values. High-risk patients should be given antibiotics to prevent bacterial infections.
Intensive dental hygiene and careful wound disinfection in the throat area play an important role here. In the first few weeks after the surgical procedure, rotational movements and transverse loads on the chest and heavy work should be avoided. Shorter flights are possible, but long-distance travel is not recommended for up to six months after the operation.
Sporting activities should initially be limited to easy hikes, cycling and swimming. If chest pain occurs or if the patient finds the feeling of constriction disturbing, it is advisable to consult the doctor treating you. In these cases, echo tests are a method for diagnosing possible disorders after heart valve surgery.
You can do that yourself
If a heart valve defect has been diagnosed, the lifestyle usually has to be changed. The doctor will recommend a healthy diet and regular exercise for the patient. In addition, stimulants such as cigarettes, alcohol and coffee should be avoided. Patients who are overweight must take measures to regain a normal body weight in the long term. In addition to physiotherapy, which is usually recommended to patients with heart valve defects, sports such as swimming or aqua jogging are also recommended.
Activities that put a lot of strain on the body, on the other hand, should no longer be carried out. These include bodybuilding and martial arts, but also stressful situations at work. If symptoms such as a stabbing pain in the heart, shortness of breath or tingling in the right arm suddenly occur, the emergency services must be called immediately. In most cases, this is a medical emergency that requires immediate medical treatment.
If the symptoms recur, a heart valve defect must be operated on. After such an operation rest and bed rest apply to the affected person. The heart must not be put under strain in the initial period after the operation and must be examined regularly to rule out complications. The doctor will give the patient individual measures that will make everyday life easier with a heart valve defect.