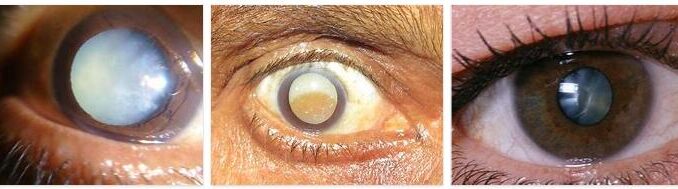
A cataract, cataract or cataract is an eye disease that can appear in people, especially in old age. This leads to a clouding of the lens of the eye. If left untreated, cataracts usually lead to blindness or severe visual disturbances. Typical first signs of a cataract are spongy and foggy looking visual disturbances and a high sensitivity to light.
What is cataracts?
According to abbreviationfinder.org, cataracts, also known as cataracts, are an eye disease in which the lens of the eye becomes cloudy and greyish. If left untreated, cataracts lead to blindness. It used to be believed that a gray liquid ran over the lens of the eye. Because of this, the disease was given the name cataract (waterfall).
Causes
In the vast majority of cases (approx. 90%), cataracts are an age-related disease that mainly occurs after the age of 65. Due to various causes, however, the disease can also occasionally occur at a younger age. These include, for example, diabetes mellitus or side effects of certain medications such as cortisone.
Years of exposure to harmful UV rays on unprotected eyes can also be a cause. A hereditary predisposition can also favor the development of a cataract. In a few cases, cataracts are congenital. The causes are diseases of the mother during pregnancy, such as rubella.
Symptoms, Ailments & Signs
Initially, cataracts cause a noticeable deterioration in vision. Accompanying this, the characteristic fog appears in the middle of the visual field, which becomes denser over time and blurs the perception. As the disease progresses, this fog spreads across the entire field of vision, causing colours, contrasts and contours to fade.
This is accompanied by a deterioration in spatial perception and thus also in the ability of those affected to orientate themselves. As the disease progresses, there is usually an increased sensitivity to bright light. Activities such as reading or watching TV are perceived as strenuous and often cause headaches and dizziness. The nature and severity of the symptoms vary from patient to patient.
In the late stages, almost all sufferers experience severely reduced vision, eventually leading to partial or total blindness. The signs of cataracts show up not only to the patient, but often to relatives and friends as well. Patients become increasingly unsafe when driving or engaging in physical activities. A strained facial expression with narrowed eyes is typical. Those affected also often miss the point when they want to pick up something.
Course
The first symptoms of cataracts are increasingly blurry, blurry vision. Signs of strong glare and reduced contrast vision also appear with the increasing clouding of the lens of the eye. The slowdown process often drags on for years.
For this reason, many sufferers only seek medical advice at a late stage of the disease. If the disease is already very advanced, the pupil appears almost white. In the final stage, it can also lead to liquefaction of the pupil and thus to blindness.
Complications
An untreated cataract leads to a continuous deterioration of vision and thus to massive limitations in everyday life for those affected. Clouding of what is seen, blurred images and refractions of light in the field of vision accumulate. The treatment of a cataract is quite low-risk.
Laser surgery now has a serious complication in less than one percent. This includes, for example, the subsequent blindness of those affected (in less than 1:1000 cases) or infections of the eye.
In about four percent of cases, a so-called secondary cataract occurs, which manifests itself in symptoms similar to those of the cataract itself. However, it can also be removed.
There are also hardly any complications associated with a lens transplant. Only the loss of the eye’s ability to accommodate is lost with the use of an artificial lens. After all, it cannot do active muscle work.
After a lens transplant, those affected have a fixed distance at which they can see clearly. Depending on the situation, this must be supplemented by suitable glasses.
Slight complications, such as eye pressure fluctuations or retinal swelling, can occur in around five percent of all eye operations. However, they must be treated with medication. The risk of cataract surgery is very low. These operations represent the most common surgical interventions in humans.
When should you go to the doctor?
In the case of cataracts, it is always advisable to see a doctor. In the worst case, and especially without treatment, the disease can lead to complete blindness in those affected and should always be treated by a doctor. As a rule, early diagnosis and treatment can completely prevent possible vision problems or blindness. A visit to a doctor is necessary if the person concerned suffers from visual disturbances that occur without any particular reason and relatively suddenly.
As a rule, vision decreases and double vision or blurred vision occurs. However, high sensitivity to light can also indicate the disease and should be investigated. Diagnosis and treatment is carried out by an ophthalmologist.
In acute emergencies, the hospital can also be visited. Since the disease can also lead to psychological problems or depression in some cases, a psychologist should also be consulted. Psychological treatment is particularly advisable in the case of complete blindness or severe visual problems.
Treatment & Therapy
Cataracts cannot be cured with medication. The only option is surgical replacement of the eye lens with an artificial lens. The surgical procedure is now a routine procedure and involves only limited risks. The surgical procedure is performed under local anesthetic and takes about 20-30 minutes per eye.
A distinction is made between two surgical techniques. In the majority of cases, the extracapsular method is used. The lens capsule is opened, the diseased lens is shattered using a laser beam and then suctioned off. In the intracapsular method, the entire lens capsule is removed. This method is rarely used anymore because it carries more risks than the extracapsular method.
After removing the clouded lens, there are several options. The most optimal and in most cases used option is the insertion of an artificial lens, which is made of plexiglass, silicone or hydrogel. Modern multifocal lenses have been used for some time, so that those affected no longer need glasses after the operation.
Slight glare and reduced contrast vision, especially at night, can still remain. Another advantage of the artificial lens is that it never has to be replaced, but remains in the eye for life.
Wearing contact lenses is an alternative to using an artificial lens. This option is only used in medically justified cases. The method of choice is the insertion of an artificial lens. After the operation, the eye needs about one to two months to heal. During this period, no heavy physical work or sports should be carried out, which increases the pressure in the eye. Swimming and saunas are also not appropriate during this time.
Forecast:
In most cases, the results of a cataract operation are so good that those affected achieve almost full visual acuity after the operation. However, if other eye diseases are also present, it may be necessary to wear glasses or contact lenses after the operation.
Outlook & Forecast
The prognosis for existing cataracts can be very different. Due to the fact that the metabolic processes in the eye are very individual, an exact prognosis is not possible. It can only be assumed in any case that the visual acuity will continue to deteriorate if the condition is not treated. It is also unlikely that the eyes will heal spontaneously. Blindness occurs after an indefinite period of time.
However, the prognosis with treatment is good. In this way, around 50 to 100 percent of the visual acuity can be restored in patients who only have one cataract. If other eye diseases, such as glaucoma, are also present, the prognosis is somewhat worse. The prognosis is also worse in the presence of degenerative eye diseases that first led to the cataract.
A so-called secondary cataract can also occur after successful treatment. This can occur months or years after treatment, but is easily treatable. The occurrence of a secondary cataract can never be ruled out.
No symptoms are to be expected after the treatment of a cataract. The artificial lens lasts a lifetime and does not cause any discomfort. There is also no foreign body sensation in the eye to be expected.
Aftercare
After cataract healing surgery (cataract or laser surgery), a bandage is placed over the eye to prevent irritation. Nevertheless, no cosmetics or similar should come into the area of the bandage. However, even after the bandage has been removed, the eye should be rested and protected from possible irritation.
Therefore, physical exertion such as sport or physical work should be avoided at first. This can increase the pressure in the eye, which can lead to risks for the recently operated eye. Likewise, no activities should be carried out where dirt or dust can collect in the eyes. After the operation, wound healing is supported by appropriate eye drops.
However, regular follow-up visits to the ophthalmologist with appropriate checks and measurements are particularly important. Although the optician can also measure your eyesight, only the doctor can monitor the healing process and tell you when you can resume all physical activities as usual.
In addition, an ophthalmologist can recognize possible risks such as a “secondary cataract”. As a rule, you can also order new glasses four to six weeks after the operation, when the eye has become accustomed to the new artificial lens.
You can do that yourself
The time between cataract surgery can be bridged with a few measures to make everyday life easier.
Wearing a peaked cap, baseball cap, or wide-brimmed hat reduces glare when outdoors. Sunglasses can be worn instead of or in addition to the hat.
It is very likely that the visual acuity will decrease somewhat by the time the cataract is ready for surgery. It is therefore important to structure your home and workplace and to create contrasts. In this way, the table can be laid in a way that is rich in contrast. High-contrast tableware is suitable as a contrast to the table. Another variant are high-contrast coasters for the dishes. Colored tinted drinking glasses are commercially available.
They help to better identify the glass and avoid accidental knocking over. Another way to avoid knocking over the glasses is to move your palm sideways, touching the table, forward and feeling the glass at the bottom. The angle at which the shoulder joint, elbow and wrist work can be easily memorized.
For cooking, the required amount of spices can be poured into the palm of your hand. The level of liquids in a container is easy to hear: the higher the liquid level in the container, the higher the tone. In addition, the time that elapses when the tap is turned on can be noted.
Temporary magnifying vision aids may be necessary. The myopic cataract patient sees better if he gets close to the object and takes off his glasses.
